The Sustainable Development Agenda for 2030 was signed during the 70th session of the United Nations General Assembly (2015), in which goal number 7 aimed to “ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all” [1]. Unfortunately, energy policy has recently suffered a radical U-turn. In Europe, most energy plans have been adversely affected by the Covid-19 pandemic, gas market volatility (2021, [2]), and also by the current war between Ukraine and Russia; from geopolitics led by international oil and gas companies to a more fragmented effect led by renewable technology suppliers, all competing for the best positions in the ongoing energy transition [2]. The war is pressuring energy security to save the economy, which leads to implementing short-term measures to enhance fossil fuels and supply routes for critical materials. For example, the revival of coal and delays in nuclear phase-out are part of the negotiations on ways to overcome the dependence on natural gas [3]. What is more, the pandemic has highlighted the inequality of access to basic energy services and the need to rethink our consumption patterns [4].
The international context requires an in-depth analysis to properly assess policymakers, and the integrated assessment modeling community is today an essential source of knowledge at this level [5]. This community develops global models aimed at covering human-Earth metabolism in long term scenarios (decades and centuries). The outcomes are aimed at deducing the best policy, given specific global goals. The complexity goes from relatively simple models, such as versions of World-3 [6], to new projects that include the disaggregation of several industries, detailed representations of the energy sector (e.g., heating & cooling degree days) [7], availability of resources [8], and such complex indicators as the dynamic EROI [9]. Indeed, the IPCC and European energy and climate agencies use these tools to shape their official reports and communications ([10], [11]).
Given the holistic insight and long-term context of IAMs, these models are used to concentrate efforts on major drivers rather than on short-term effects. This is the case of the power system, where fast variations in generation and demand deeply modified annual indicators. For example, seasonal average (SA) and LCOE (simple aggregation methods) overestimated the expansion of installed capacities and value of variable renewables, while underestimating the dispatchability feature of some units [12]. The proposed 100% CO2 cap scenario showed 24% of generation coming from electrolysis, battery storage and nuclear in the model with 8760 hours; while SA showed only 3% and LCOE did so close to 1%. Shirizadeh et al. [13] reported that an energy system optimization model configured a set of time steps (1 h, 2 h, 4 h, 8 h) to show discrepancies in the energy mix, system cost, and CO2 emissions. Errors reached values above 2% in solar-PV, CCGT, nuclear production, and thermal and electric storage (2 h resolution, related to 1 h). Errors were exponentially increased with higher time aggregations. Finally, another study concluded the following points regarding temporal aggregations compared to the hourly resolution, especially under deep decarbonization pathways [14]:
Alter generation mixes, varying approach and policy stringency.
Overestimate the capacity contribution and the value of resources (especially VRES), therefore underestimating the services of dispatchable power plants. A high impact was found in the shares of nuclear, hydrogen, and battery storage in the generation, as well as in interregional transmission requirements.
Simple approaches save investment in firm capacity relative to hourly analysis.
Aggregation errors increase at higher decarbonization levels.
Wide-ranging problems need ample perspectives. The concept of smart energy systems sets a “scientific basis for a paradigm shift away from single-sector thinking into a coherent and integrated understanding of how to design and identify the most achievable and affordable strategies to implement coherent future sustainable energy systems” [15]. This relatively novel concept in energy planning follows a similar system of thought to the IAM community, in that modelers focus attention on the relationships among agents and simulate the behavior of the whole system in order to learn about it and understand the main consequences of policies in their respective scientific questions. A hot topic in the field of smart energy systems is the integration of fluctuating renewable energy sources through energy converters to create a realm of flexibilities across productive sectors and end-use substitutions.
Given these differences, the community of energy modeling has criticized the lack of hourly/intra-hourly representation of the power and heat systems. This misleading description underestimates the flexibility requirements (storage, power-to-X, etc.) in both supply and demand sides [16].
Regarding carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies, interest in them has grown sharply over the last few years, highlighting the relevance of CCS in fully decarbonized societies [17] and the lack of this option in the methods in the literature [18]. However, we have omitted them because CCS is far more expensive than renewables, has a poor economics, is not a mature technology, manages only one element (CO2) of the pollutants in power plants [19][20], and it has an extremely low or even negative net energy (EROI less than 1) ([21], and section 2.8.1. in [22]).
In 2022, G. Parrado-Hernando et al. reviewed 8 IAMs according to how the power system is modeled (tables A.1 and A.2 in [23]), reaching several conclusions. First, there is agreement on using the hourly resolution for IAMs, avoiding such aggregative methods as time slices. Second, there is no agreement on which the best method and tool would be to apply, allowing the modelers to make the selection according to multiple criteria (e.g., computational cost versus accuracy). Third, proposals currently seem to achieve further development in soft-/hard-linking of individual energy models to the IAM via an external code, instead of integrating the first code into the second. This may be due to the fact that two models usually run in two different computational frameworks; so IAMs would not be able to run the energy system on the hourly timeframe and the rest of the model on the yearly timeframe.
A qualitative comparison of the contribution presented in this work is summarized in Table 1. The model assumes endogenous feedback and power constraints that enhance the accuracy and reliability of the power system modeling in comparison to our previous work ([23] and [24]), with a small additional computational effort.
Qualitative analysis of the approach proposed in this article. Expansion of table 5 in [23]
| Criteria | This work |
|---|---|
| Potential feedback in the IAM | Yes. The approach should be included between the final and primary energy in the transformation chain. |
| Facility to include new technologies | High. More technologies can be included. |
| Accuracy | High. More accurate than slide-based approaches, less than power flow models. |
| Complexity | Medium. Only algebraic equations are required. More dimensions can be introduced in the approach (e.g., water availability in dam hydropower plants). |
| Reliability of the power system | Medium. Power ramps are not constrained. The maximum hourly generation is constrained. |
| Presence in IAMs | Not yet tested. |
| Computational cost in the IAM | Relatively fast. The power system needs to be calculated once a year, but the rest of the IAM would rely on the integration time step; so, a TIME STEP of 0.25 requires the calculation of the same power system 4 times a year. |
| Potential uncertainty analysis in the coefficients | No. This is not implicit in the method, but exogenous methods can fulfill this analysis, e.g., the Montecarlo simulation. |
Consequent to the research line, this article is focused on the following question: could IAMs work with two different time scales in the same simulation? To the extent of our knowledge, there is no IAM running as a unique code in both yearly and hourly time scales. So, the contribution of this work may be summarized as follows:
Develop a compatible computational framework of an hourly electricity system for yearly capacity expansions of integrated assessment models.
Develop a bottom-up power system model running at two different time scales, yearly and hourly, simultaneously.
Develop the technology mix in the current policy scenario of the Spanish energy transition as a case study, based on public, open-access data.
Assess the feasibility of the NECP goals, including relevant impacts in the power system.
The article is structured as follows. The next section explains the novelties, logic, and scope of the developed model, as well as the necessary materials for running simulations. Then, the results and discussion are presented together according to the features of the model and simulations of the scenarios. The last section sets out the conclusions and further work in the research line.
This section defines the equations and scope of the model HPSS, as well as the materials required to calibrate the model for the Spanish case.
An overview of the whole approach is presented in Figure 1. The main novelty of HPSS is the use of the subscripting feature, i.e., an array structure of elements that can be repeated as many times as the modeler needs. Taking advantage of this feature, the dispatch of electricity is configured through variables containing subscripts of 8760 elements (the hours in a year). These are used to import the hourly profiles of demands and VRES, calculate the intermediary steps, and report hourly indicators of interest, such as curtailment† or power ramps. Concurrently, the integration method solves the differential equations that represent the dynamics of the capacities of technologies, the evolution of efficiencies, and the aggregated indicators over time. Consequently, subscripts have generated the ability to represent two or more discrete temporal dimensions while the continuous integration process is ongoing. This idea is not new and has been employed in other dissimilar fields facing similar problems, e.g., irrigation [25] and migration [26].
General overview of the HPSS model. Yellow variables are calibrated for the base years. Grey boxes are exogenous data; while blue boxes are exogenous data in this work, but endogenous in an IAM (to be endogenized in further work). The equations set out in this work are summarized as “Addition” or “Subtraction” in the gray color. The two intermittent boxes are variables repeated to clarify the diagram. It is well known that “the system must be able to meet the continually changing load demand” [28], verifying the first property of the allocation function.
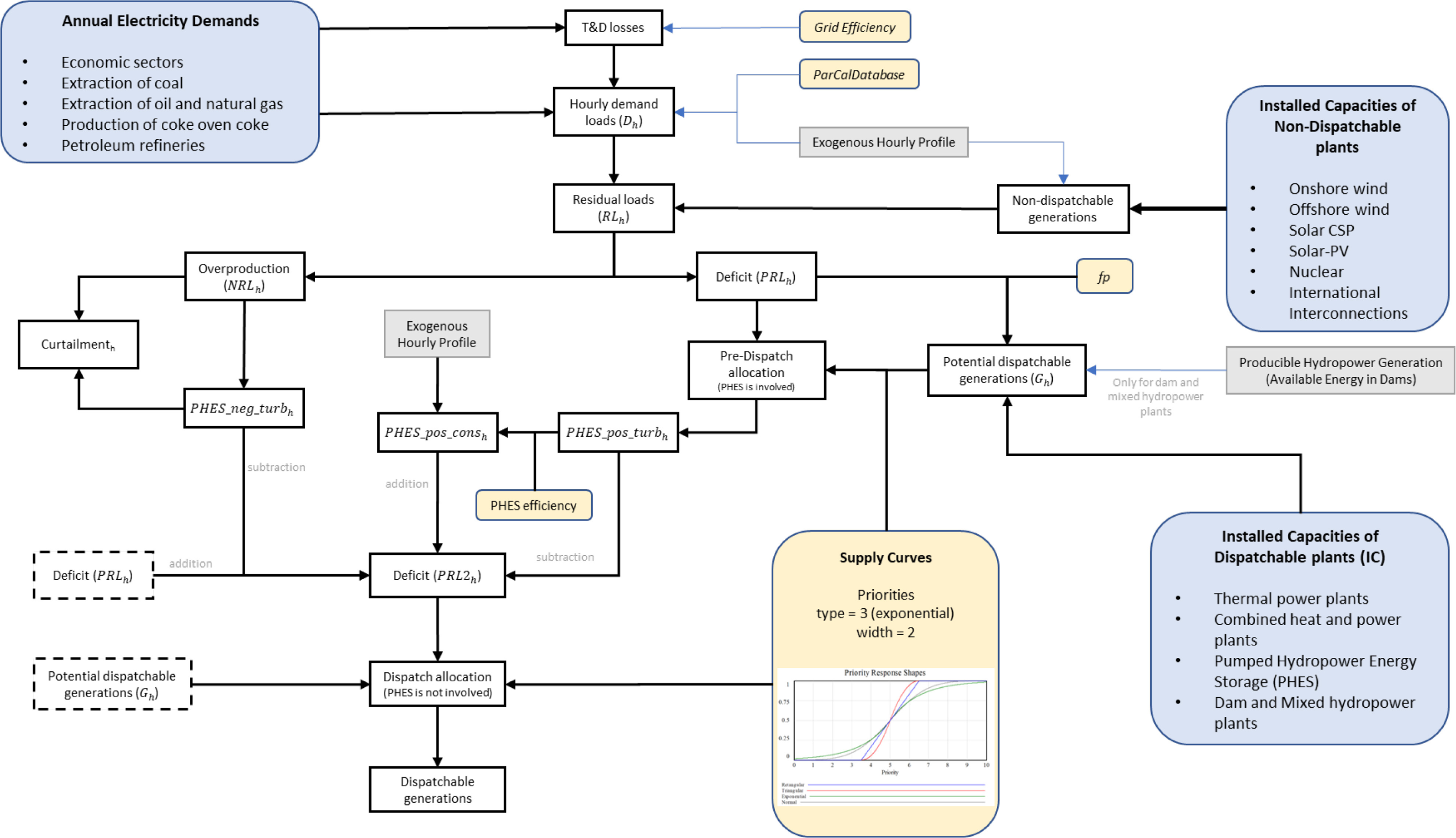
Nevertheless, the question about the dispatch of electricity that needs to be answered is: How can the load demand be fulfilled from different suppliers? Here, the one-to-many allocation function takes place. It is a mathematical formulation that solves a single market, where several suppliers are trying to satisfy the demand. In this work, the functionality reproduces the operation of the power system every hour. The software used to develop the model is Vensim DSS, where the “ALLOCATE AVAILABLE” function is included in the software set [27]. In short, the allocation function has six properties implicitly assumed and specified for our problem:
Conservation of matter: the amount received by the demanders has to be equal to the amount managed by the suppliers.
Nonnegative values: all the quantities must be equal to or greater than zero.
Conservation of intent: no supplier shall provide more than the desired/possible amount of energy to supply. Similarly, no demander shall receive more than what has been chosen.
No loopholes: under adequate conditions, each agent should receive/supply its stated demand/offer.
Differentiation: in the case of energy shortage, extremely low priority agents should receive/supply little or nothing and extremely high priority agents should receive/supply a higher amount of energy or almost everything.
Continuity: with small changes in priorities, supply and demand should cause small and smooth changes in the resulting allocations.
The non-dispatchable generation (VRES), nuclear (N), imports (I), and exports (E) load is subtracted from the load demand (D) in order to place the difference (residual load) in either a positive or negative distribution (RL). This concept of residual load (RL) [29] has been used to fulfill the second property throughout equation (1) (where h corresponds to each hour). Positive values (PRL) correspond to hours with a deficit of energy before management; while negative values mean over-productive hours (an excess of electricity). Both resulting positive and negative distributions are treated as separate markets to define which technologies can respond by covering the deficit (e.g., thermal power plants), increasing the load demand (e.g., heat pumps), reducing the generation (e.g., curtailment), or influencing both markets (e.g., storage).
(1)
The maximum load of the suppliers is limited by the installed capacity of the technology in the year (IC) and, in the case of hydropower units, the maximum hourly producible‡ profile.
On the other hand, every dispatchable power plant has a range of technical flexibility to offer an hourly potential generation (Gh) due to the inertia of the heating system and the turbines, thermal stress and security risks, among others (section 2 in [30]). So the generation of electricity is partially restricted so as to reproduce the adaptability of the system following the demand, an effect also related to the schedule that suppliers create with the objective of maximizing profits. This effect is reproduced with equation (2) in the model, which divides the generation into a flexible load and an invariable load controlled by a flexibility parameter (fp). An exception has been introduced for the case of storage, which is explained later. This method respects the third and four properties of the allocate function that is applied later.
(2)
Competition for the demand load is present in any liberalized electricity market. A priority according to the technology is assumed in order to manage the energy shortages in hours when the aggregated desired supply is higher than the load demand. This effect is property number 5 of the allocate function. In this work, the priority is an indicator of how good the position of a supply technology is in the electricity market. The higher the priority, the higher the energy delivered. Since the suppliers cannot deliver more energy than the demand, a smaller load implies more competition. Finally, the model assumes that small modifications in priorities deliver small changes in the resulting supply mix; given that the hour, as a time unit, is sufficiently short as to assume smoothness in the energy delivery. This continuity is achieved by applying an exponential function to the shape of the priority response for the supply curves (green line in the graph of Figure 1).
Pumped hydropower energy storage (PHES) has been modeled in a singular way to avoid simultaneous equations in the code. From the literature, the knowledge states that: a) these units pump water during off-peak hours (low demand) and turbine water afterwards during peak-hours [31]; b) they cover from daily to seasonal cycles [31]; c) they can offer primary and secondary ancillary services to obtain profits, added to those obtained from the intraday and day-ahead markets (increasing profits compared to traditional bidding [32], even double [33]). The behavior of PHES becomes even harder in potential smart energy systems prepared for a high, or even 100%, renewable share in the energy system, where more technologies may offer similar services (vehicle-to-grid) and competition for the renewable overproduction [34]. Representing the totality of this complexity falls beyond the scope of this work; however, some operational details have already been integrated to show the potentialities and barriers in modeling.
First, an estimation of the generation mix, which we called hourly pre-dispatch, is calculated by an allocation function to get the share of the positive residual load pumped to the storage from the market competition (PHES_pos_turb). As a consequence, the annual consumption of the pumping mode is calculated with the efficiency of this technology (eq. (3)). Then, this consumption is split into 8760 hourly loads based on its historical profile (PHES_pos_cons).
(3)
The consumption of the pumping mode is added to the load demand for a second allocation (dispatch) where, since it has already been accounted for, the turbine mode of PHES is not involved (LD_2nd_al). In short, the pre-dispatch is used as a kind of forecast to depict the turbine and pumping patterns of PHES. This pre-calculation avoids simultaneous equations.
As for the negative residuals (excess of electricity), storage is the only technology able to make a profit in this version of the model, a clear advantage in scenarios with high shares of non-dispatchable contribution. Thus, PHES acts as a monopolistic agent, pumping as much energy as possible (PHES_neg_turb). In this case, the consumption during the pumping mode does not increase the base load demand in hours with a deficit of energy, since the negative value is potentially curtailment. On the contrary, this storage technology transfers energy from the negative to the positive distribution, so the positive value of the load demand is reduced by a quantity equal to the overproduction gathered by storage (PRL2h in eq. (4)).
(4)
Therefore, the remaining negative residual loads (after storage) are accounted for as curtailment. Although there are other options to flexibilize the supply and demand sides facing deeper decarbonization marks, only storage has been considered due to the lack of data. Examples of other flexibility options are power-to-heat, power-to-hydrogen, or smart electric vehicles (section IX-F and throughout the text, respectively, in [34]). However, these options are residual in the historical period and data are not fully available (e.g., hourly profiles for calibration). The inclusion of more technologies in the competition for the excess of electricity is further work for the approach.
Once storage has been calculated, the second allocation re-calculates the electricity mix for the dispatchable technologies (LD_2nd_al). The priorities are the same for both allocate functions; they do not change from the pre-dispatch to the dispatch allocation or across hours.
Once the properties have been contextualized for the problem, the following paragraphs set out the technological specifications for the modeling of the Spanish power system. The dispatchable power plants (combined heat and power, CHP, and thermal power plants, PP) are sorted, in turn, by fuel: gas, geothermal, liquid, and solid fuels; as well as two hydropower technologies: traditional hydropower plants (dammed and mixed) and pump hydroelectric energy storage. In total, there are 12 technologies operating when necessary to fulfill the positive residual loads (Table 2), with a degree of freedom in the allocation mechanism, i.e., the hours when non-dispatchable generation is not enough. Table 2 also shows the coherency between databases and the HPSS model. The priorities are restricted to between 0 and 10, that is, the annual competitiveness in accessing the electricity market.
List of technologies in the HPSS model, including which are exogenous or endogenous, and the corresponding category in the data source. T&D: transmission and distribution; REE: Spanish power system operator; IDAE: Institute of Diversification and Energy Savings of Spain
| Technology | HPSS model | Data categories | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Load demand | Exogenous | Demand + T&D losses | REE |
| Onshore wind | Exogenous | Onshore wind | REE |
| Solar PV | Exogenous | Solar PV | REE |
| Solar CSP | Exogenous | Solar CSP | REE |
| Nuclear | Exogenous | Nuclear | REE |
| International Interconnections | Exogenous | Net trade | REE |
| CHP_gas_fuels | Endogenous | Natural gas + biogas | IDAE |
| CHP_geothermal | Endogenous | Geothermal | IDAE |
| CHP_liquid_fuels | Endogenous | Oil | IDAE |
| CHP_solid_fuels | Endogenous | Coal + biomass | IDAE |
| CHP_waste | Endogenous | Municipal waste | IDAE |
| PP_gas_fuels | Endogenous | CCGT + biogas | REE |
| PP_geothermal | Endogenous | Geothermal | REE |
| PP_hydropower_dammed | Endogenous | Dam and Mixed | REE |
| PP_liquid_fuels | Endogenous | Fuel/Gas engines | REE |
| PP_solid_fuels | Endogenous | Coal + Biomass | REE |
| PP_waste | Endogenous | Waste | REE |
| hydropower_pumped | Endogenous | Pump hydropower | REE |
Hourly generation profiles of VRES, nuclear and international transactions are exogenous inputs introduced due to the high uncertainty around them. Forecasting techniques have been developed for different time frames. However, the behavior of solar irradiation and wind speed predictors remains unclear beyond 2 days ahead [35], while climate change also impacts the availability of resources in the long term [36][37]. Finally, international power exchanges and nuclear power plants are running under strict bilateral agreements to exchange electricity between different markets, making their profiles harder and unclear. The dynamics of human-decision-based generation, as well as the dynamization of the VRES profiles, are beyond the scope of this work. As mentioned later, the exogenous profiles introduced to calibrate the historical period are also used as input to select the patterns for the future context in which energy policies are to be applied.
A common way to estimate the generation is from the installed capacity. This is done via normalization. For the exogenous technologies, the hourly load is divided by the installed capacity. So, the capacity expansion proportionally determines the generation in the scenario. In equation (5), the correction parameters (CP) translate these installed capacities into hourly generations. When these values remain very close to one, it means that the databases are consistent with the hourly profiles introduced. CP values are estimated via calibration.
(5)
The independence across elements of the subscript is a limitation of the approach, i.e., an element cannot be updated or calculated based on another element. Consequently, the energy mix of one hour cannot be used to calculate the following one. This implies that the turbine/pumping mode of hydroelectric plants, for instance, cannot be constrained by the level of water in the up and down reservoirs.
However, this limitation is partially solved after the allocate functions. The maximum power ramps in the year are estimated from the hourly generations so as to deliver an indicator of the necessary technical requirements, which may validate the scenario or not. A similar reasoning may be followed for the hourly exchanges of water.
The electricity demand follows the Eurostat’s convention on energy balances. The data are exogenously imported from 24 economic sectors, including the energy sector; which are then sorted into the extraction of fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, oil), consumption to produce coke oven coke for the steel and iron industry, and petroleum refineries. The transmission and distribution losses increase the electricity demand up to the demand at the busbars of the generators. A parameter multiplies this last demand to meet the demand from all databases (ParCalDatabase). As is shown in the next subsection, this multiplier matches the annual demand provided by the energy balances of Eurostat and the value reported by the power system operator, REE.
This section sets out the data sources used to study the Spanish power system with HPSS.
The annual consumption of electricity by the economic sectors and transmission losses have been gathered from Eurostat [38]. Moreover, the hourly profiles of the technologies have been collected from the power system operator’s database (ESIOS, [39]). Together, they make up the main data source.
Water resources, evaluated as producible energy, are extracted from the AEMET reports on a daily basis [40]. The estimation of the hourly potential for dammed and mixed hydropower generation is homogenously distributed over the day, so the daily value is divided by 24 hours.
Additionally, the data related to combined heat and power (CHP) generation has been found in a complete report written by the Institute for Energy Diversification and Saving (IDAE, Spanish acronym) [41]. Facilities are categorized by technology, sector, and fuel, including the installed capacity, electricity production, fuel consumption, and net heat production. There is a lack of information about residual generation in Spain from marine, solid biofuel, renewable municipal waste, and liquid biofuel.
Finally, the power system operator (REE) annually delivers reports [42] with Excel files that have been used for calibration purposes. For example, electricity generation by technology, including the net international balance and pumping hydropower consumption.
This section covers the calibration of the HPSS model in the historical period, providing information about the priorities of dispatchable power plants and the efficiency of pumped hydropower energy storage. Then, the NECP’s objective for the power system by 2030, i.e., the percentage of renewable energy in the electricity mix, is evaluated in a baseline scenario and achieved in an alternative scenario.
The availability of data in Spain has allowed us to study the calibration of most of the parameters over four years, from 2017 to 2020. This period is characterized by dissimilar meteorological conditions, the deployment of solar and wind (38%), the decommissioning of coal power plants (40%), and the disruptive effect of the Covid-19 disease in 2020.
Unfortunately, geothermal, run-of-river, oceanic, solar urban and offshore wind generation are negligible in Spain, there are no data about their hourly profiles. Consequently, they were not considered.
Powell’s algorithm is a hill-climbing method (iterative) that finds a function’s minimum value by sequential one-dimensional searches using the concept of conjugate directions [43]; the lack of gradients in this method is useful for non-differentiable and differentiable functions [44]. The Powell method was selected to calibrate and manage the priorities of the power system. This method is a Vensim software tool, explained in the documentation [27] and in specific publications [45][46]. The optimal values of priorities that minimize the payoff function are specified in Table 3; while the results of the calibration are shown in Table A. 1. As mentioned above, the priorities are constrained between 0 and 10 for the calibration of the allocation functions.
Values for the Powell algorithm
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Weight | 1 |
| Vector points | 25 |
| Maximum iterations | 1000 |
| Pass Limit | 2 |
| Fraction tolerance | 0.00003 |
| Absolute tolerance | 1 |
The parameter that evaluates the consistency between Eurostat and the power system operator database is very close to one in all the years (ParCalDatabase). So, there is perfect consistency between official agencies.
The hypothesis of assuming equivalence between the hourly average power and hourly generation is also acceptable, given the closeness to one in the results of international trade, wind, solar, and nuclear generation. Therefore, the estimation of the yearly generation from the hourly power profile and the installed capacity of the technology is also accepted.
However, the dimensionality of the problem has been simplified, i.e., the number of degrees of freedom in the calibration algorithm, in such a way that the maximum potential load generated by the dispatchable power plants corresponds to the installed capacity (fp = 0). Further analysis is required to explain the constraints in the generation of these technologies.
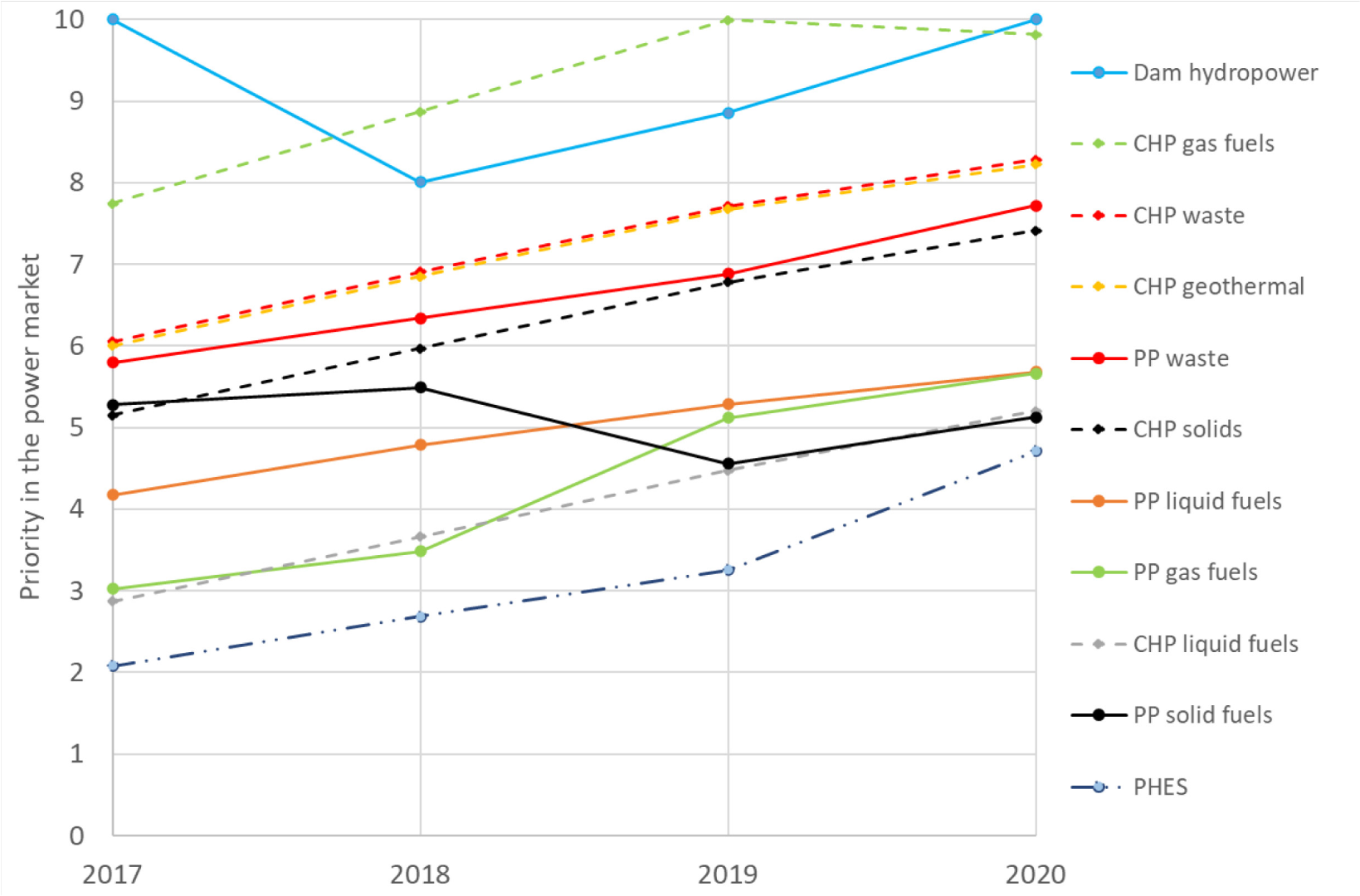
Figure 2 illustrates the priorities of dispatchable power units. Dam hydropower and CHP fueled by gas units are at the top of the electricity market in Spain, while the pumping mode of hydropower and PP units (traditionally run by fossil fuels) are at the bottom. The range of dots is narrower over time, which indicates that the market evolved towards a more competitive scenario. In the ranking, there is a significant change between 2018 and 2019, when PP solids (mostly coal) experienced a depletion in the installed capacity, promoting the role of other technologies, such as PP gas, CHP liquid and PHES, to replace it. Finally, the disruption of the Covid-19 disease did not affect priorities, indicating that these are driven by technical reasons of the suppliers rather than the electricity demand pattern.
Priorities of dispatchable power plants in the historical period
The historical round-trip efficiency in PHES units was found to be between 54.3-61.2%, far below the common range of values in the literature (70-80%, [31]). As for the power network, the technical and non-technical transmission and distribution losses§ have increased over the historical period from 9.8% to 11.4% (Eurostat). The reasons behind this increasing inefficiency are beyond the scope of this article.
Equation (6) accounts for the error in all the results of interest. Percentages between the actual and the calibrated annual generations are reported in Table A. 2, where all of them fell far below 5%. “CHP waste” delivered 4.04% more energy than expected in 2020; however, its generation is very low in relation to the total amount supplied (around 0.07%). The deviations in the share of renewables are +0.33% (2017), -0.09% (2018), -0.37% (2019), and -0.96% (2020). The highest error for PHES was only -1.21 MWh (2019). In agreement with the Spanish power system operator, PHES was considered a non-renewable energy source. Furthermore, when a set of technologies is mixed in the same category of the model, the installed capacity of each technology is used as a proxy to make the generation share, e.g., biomass represented 15.57% of the “PP solid fuels”, while biogas 1.01% of “PP gas fuels”, in 2020.
(6)
Table A. 3 shows acceptable errors for the purpose of the model. As can be seen, most of the means of the errors are very close to zero, apart from PP_solid & PP_waste, probably caused by the lack of disaggregation of these technologies in ESIOS. In short, the low errors in the model parameters validates the accuracy, given the available knowledge and data.
The rest of this subsection tests the behavior of the model when facing changes in two sensitive variables: First, the installed capacities of nuclear power plants; and second, the priority of PHES. In order to better visualize non-linearities in the results, the expansion of installed capacities and priorities follows a future linear trend. For the same reason, the demand remains constant over time and equal to the corresponding value of the historical year (268 TWh, 269 TWh, 265 TWh, 250 TWh, respectively).
The first exercise phases out the nuclear power plants by 2030. Meanwhile, the priorities remain constant and equal to the corresponding historical year. Four future trends are obtained, shown in Figure 3. The brown vertical line separates the historical period from the future.
Evolution of some suppliers for different historical conditions. One color by year and one type of line by technology. The brown vertical line separates the historical period (left, one known point per year) from the scenario (right, four possible points per year)
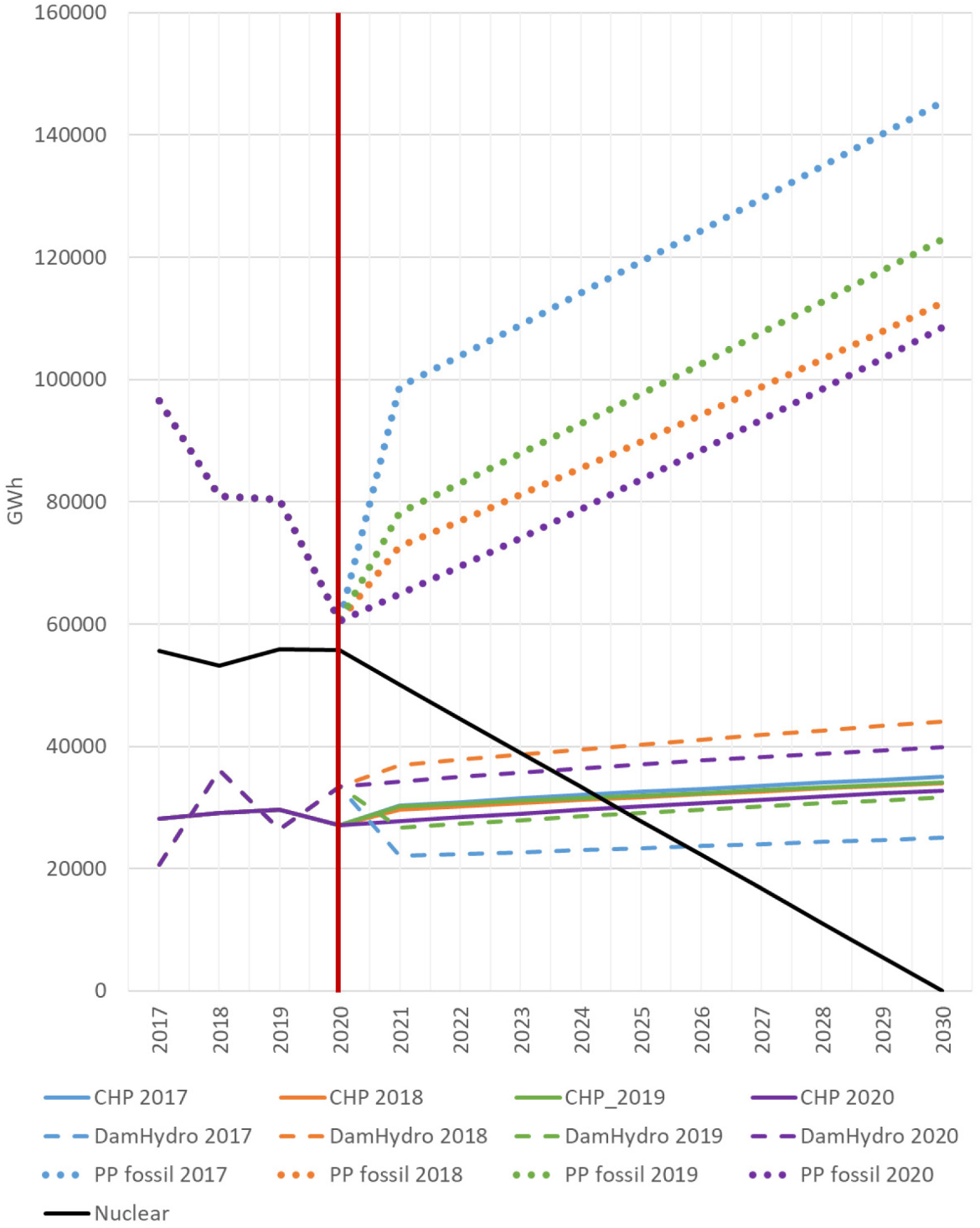
The profile for nuclear power plants is exogenously assumed, and is therefore inflexible. This situation creates a reaction of dispatchable power plants, increasing their generation to fulfill the gap. The year 2017 was a dry year; therefore, hydropower generation barely grew over time (dashed blue line), being substituted by fossil fuels in thermal power plants (blue dash-dot line).
The political-medical decision for a lockdown due to the Covid-19 disease (2020) provoked a drastic reduction in the electricity demand, especially in households. It implied less energy consumption from fossil fuel power plants, but also higher hydropower generation, given the favorable hydrology of that year.
The second exercise plays with two trends for the priority of pumped hydropower energy storage. The first linearly changes the priority from 2020 (4.71) up to the maximum (10) at the end of the simulation (2030). The second keeps the priority of 2017 constant. Additionally, the installed capacities of VRES are expanded 2.36 times in the same period to generate more over-productive hours in the year, stimulating PHES. For all the future years, the rest of the parameters remain constant with the calibrated values of 2017.
Figure 4 reveals the impact of the growth of the variable renewables introduced in the scenario. The expansion leads to a high amount of curtailed energy, reaching around 8% of the electricity demand by 2030. The PHES-priority trend with increasing values (“increasing” label in the figure) covers higher market shares in the electricity mix. However, the consumption related to the pumping mode increases, which leads to higher generations of other dispatchable plants at certain hours to cover the increments in the load demands (CHP, dam hydropower, and fossil fuels).
Evolution of some suppliers and curtailment facing a renewable growth. The brown vertical line separates the historical period (left, one known point per year) from the scenario (right, two possible points per year). “_increasing” points out variables of the scenario with increasing PHES priority (up to 10 by 2030)
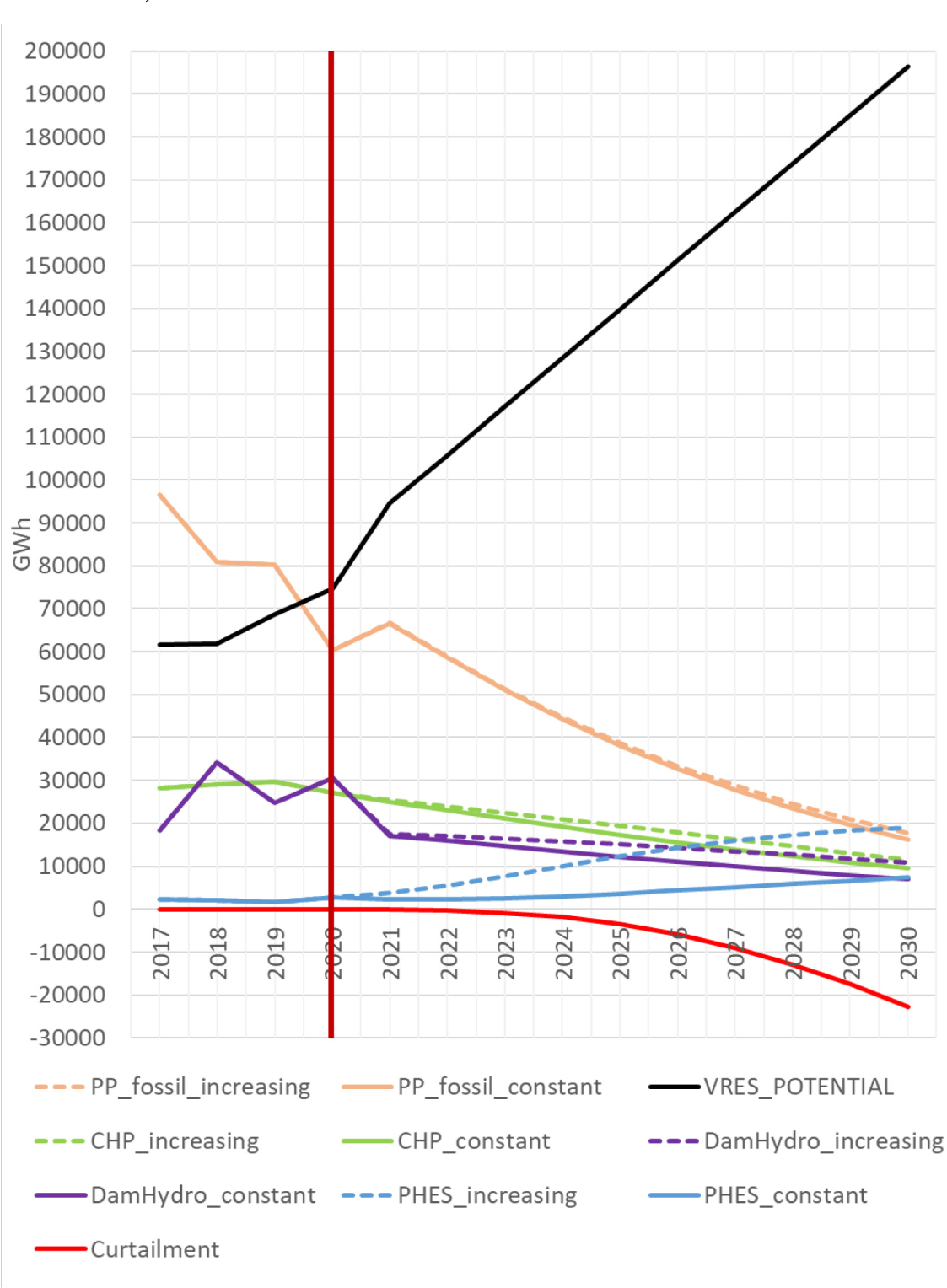
The positive residual load value (PRL) in over-productive hours is zero, so the potential generation of PHES is entirely available for the negative RLD market. This is why PHES has a privileged role in the system. Consequently, the priority of the pumping mode power does not affect curtailment. The effect on curtailment comes from the installed capacity of this option.
The priorities of installed capacities are used as previously to reproduce different historical conditions (2017-2020). These conditions are assumed to justify legislative and technical dynamic processes, allowing us to estimate a range of potential benefits when promoting one or other technology over the energy transition.
This subsection analyzes the objective scenario of the Spanish NECP [47], an integrated report to meet the EU’s climate and energy targets for the period from 2021 to 2030 (EU/2018/1999). The values and correspondence across categories to adapt the HPSS model to the NECP are shown in Table 4. Priorities are not moved after 2020, running four simulations according to the historical years previously calibrated.
Installed capacities in the power system for the objective scenario of the NECP (2030) [47]. Translation to HPSS categories between brackets. Units of installed capacities in megawatts (MW). Electricity demand in terawatt-hour (TWh)
| Electricity demand (in central bars) | 346.29 TWh |
| Technology | Capacity [MW] |
| Wind (PP_wind_onshore) | 50333 |
| Solar-PV (PP_solar_PV) | 39181 |
| Solar CSP (PP_solar_CSP) | 7303 |
| Dam+Mixed hydropower (PP_hydropower_dammed) | 17296 |
| Storage (hydropower_pumped) | 6837 |
| Biogas (PP_gas_fuels) | 241 |
| Biomass (PP_solid_fuels) | 1408 |
| Coal (PP_solid_fuels) | 0 |
| CCGT (PP_gas_fuels) | 26612 |
| Fuel/Gas (PP_liquid_fuels) | 1854 |
| Waste & others (CHP_waste) | 341 |
| Nuclear (PP_nuclear) | 3181 |
| Cogeneration (CHP_solid_fuels) | 3670 |
| Other renewables (CHP_geothermal) | 80 |
| International Interconnection | 11800 (8000 with France, 3000 with Portugal, 800 with Morocco) |
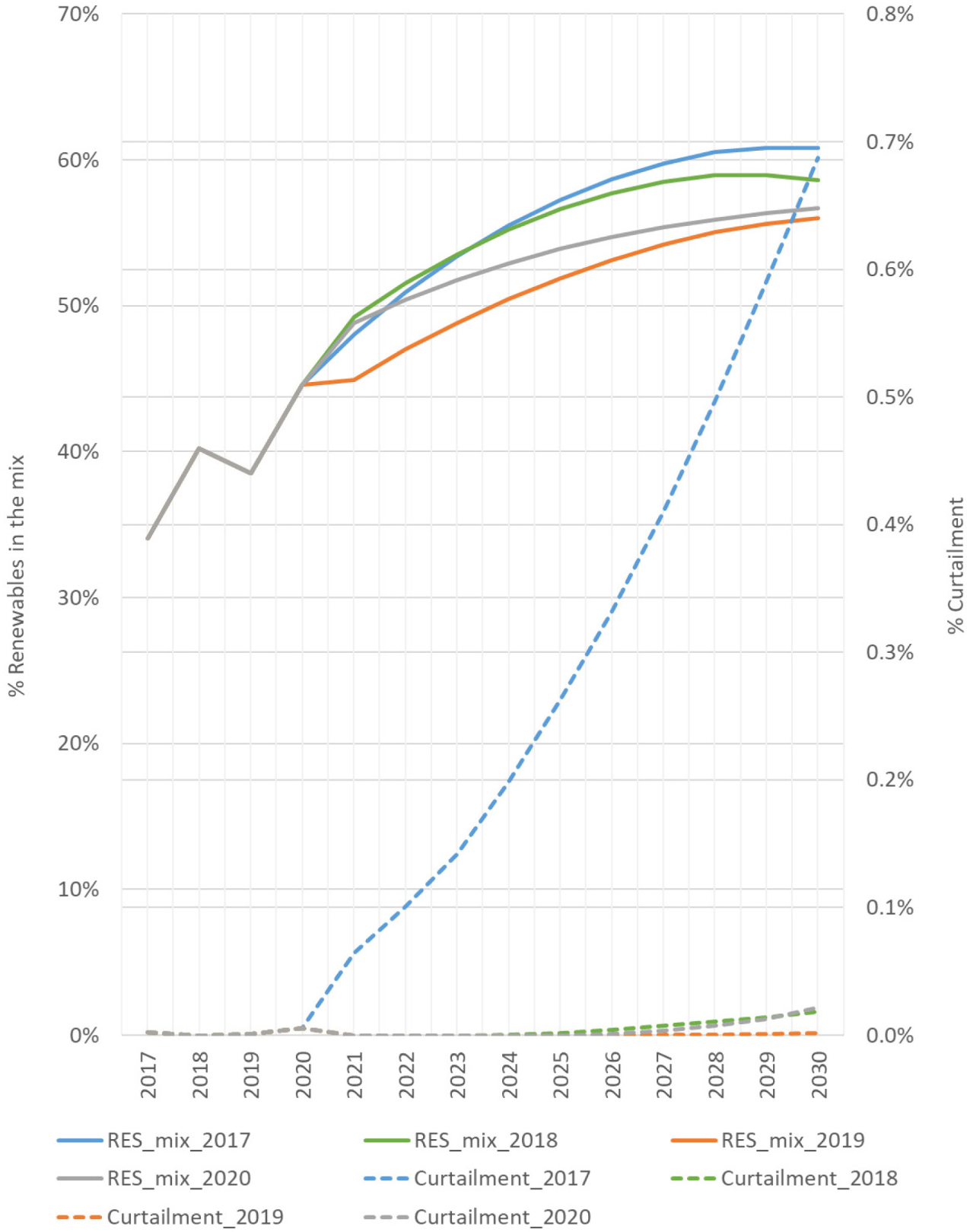
As can be seen in Figure 5, renewables do not go further than 61% in the share of any of the four simulations. This finding relies on the specific context, i.e., the NECP Spanish report, and it may be different from one region to another. For example, a recent study achieves a renewable penetration of 80% in the electricity mix when simulating the official Danish pathway to 2030 (objective of 70% reduction in the greenhouse gas emissions) [48]. On the 2030 Australian power system represented by De Rosa et al. [49], the indicator was estimated in the range of 21.4-36.3%.
Curtailment increases with the higher penetration of variable renewables. This is caused by the lack of sufficient flexibility in the system to integrate the excess of non-dispatchable electricity production into new demands in other energy sectors, such as heating and transport. In addition, the whole 2017 was very dry, so very productive for solar and unproductive for hydropower plants. This combination generates a less flexible hourly profile in the supply side of the power system. Most of the overproduction is therefore used by storage. The profiles of nuclear and international interconnections are exogenous, a fact that further contributes to increasing the likelihood of over-productive hours. Fortunately, although the conditions of 2017 seem to be harder than other historical years, curtailment does not so increase very much, wasting energy in 519 of the hours in 2030 (1.4 % of the VRES generation) in the worst case.
The progression of renewables in the mix reaches an upper limit. This suggests additional installations of flexibility options to further integrate the excess of electricity production and avoid carbon emissions.
Percentages of renewable share in the mix and curtailment (related to VRES generation) for the NECP scenario, based on the 4 historical years
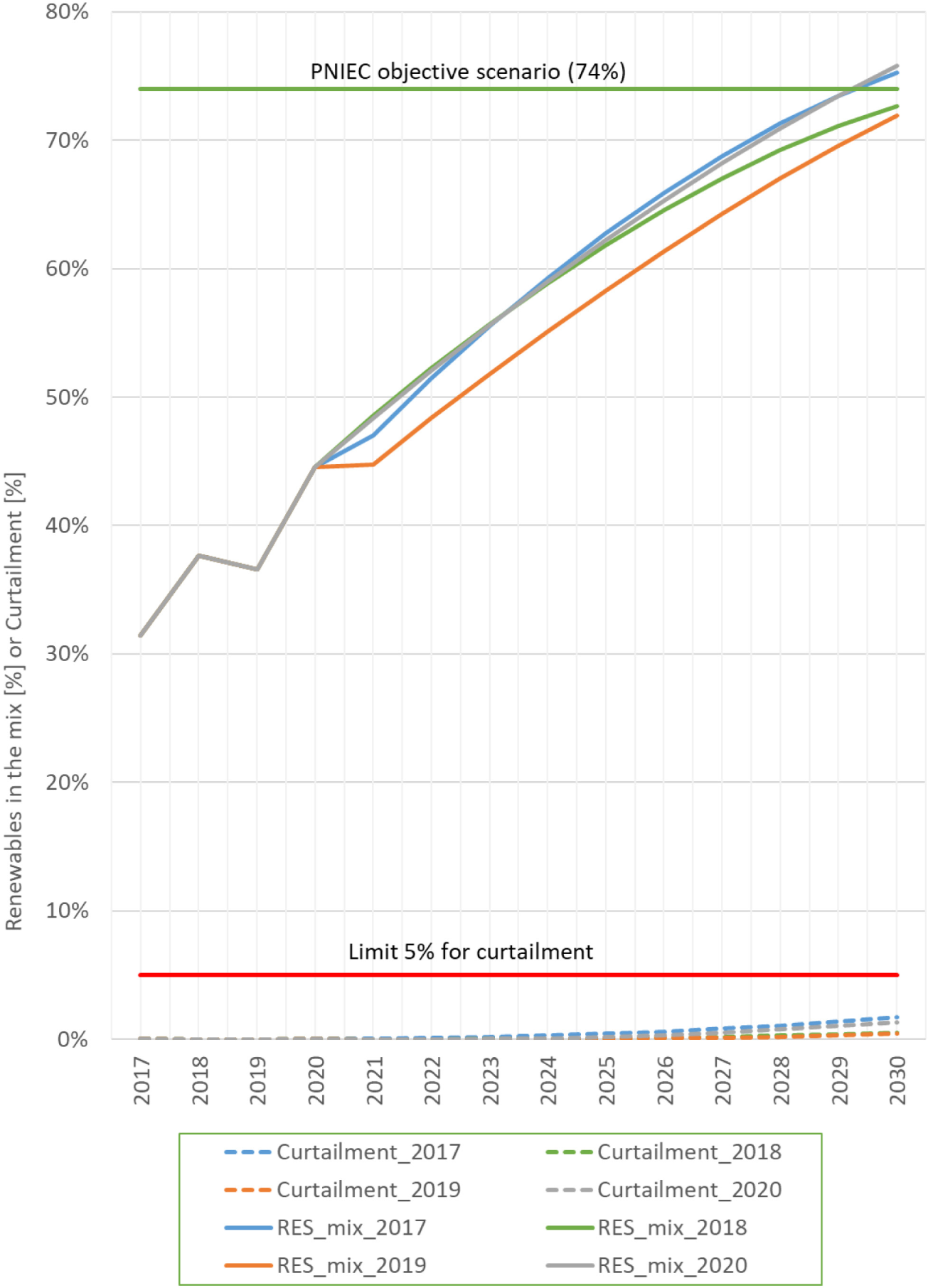
The last simulation evaluates a way to achieve the objective of a 74% renewable share in the Spanish power system. This plan assumes the following measures:
Constant electricity demand over time.
Reduction of the international interconnection capacity to test the Iberian case, given “the lack of a coordinated common energy policy with its neighboring systems” [50].
Decommissioning of nuclear power plants, since they introduce inflexible generation into the model.
Finally, the optimal ratio wind/solar-PV of 1.86 is applied from the literature [51]. This ratio reduces the statistical renewable variability burden by installing infrastructure according to the regional conditions of Spain (59520 MW and 32000 MW, respectively, by 2030).
The resulting share of renewable electricity in the mix is shown in Figure 6, where 1.7 % of its generation would be curtailed in the worst conditions (2017), and which is far below 5%, a standard limit in the literature of energy planning [52],[53]. Statistically, the conditions for 2017 and 2020 would help more than those of 2018 and 2019, to reach the objective.
Proposal of scenario for Spain between 2020-2030. Percentages of renewable share, percentage of curtailment (related to VRES generation), based on the assumption of 4 different historical conditions
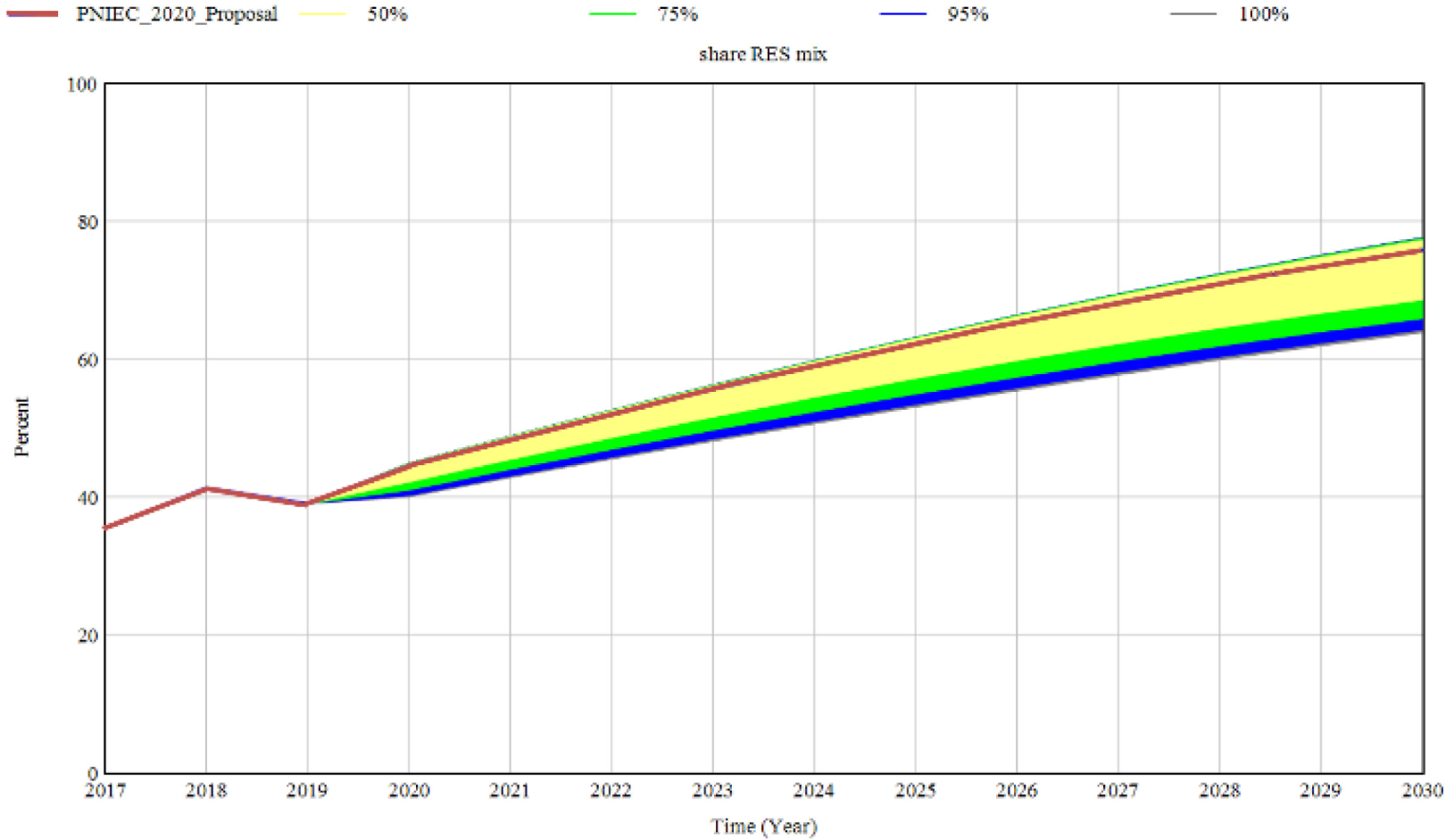
As shown before, the generation of PHES is sensitive to changes in its priority. One way to address the uncertainty of this model parameter is through sensitivity simulation [54]. Uniform distribution from 1 to 10 is applied to the PHES priority to generate 2000 simulations. Figure 7 shows a likelihood range between 63-78% in the share of renewables in the mix, highlighting a significant influence of this technology when its priority is widely modified.
Sensitivity analysis to the PHES priority from 1 to 10, with a total of 2000 simulations performed by a random uniform distribution
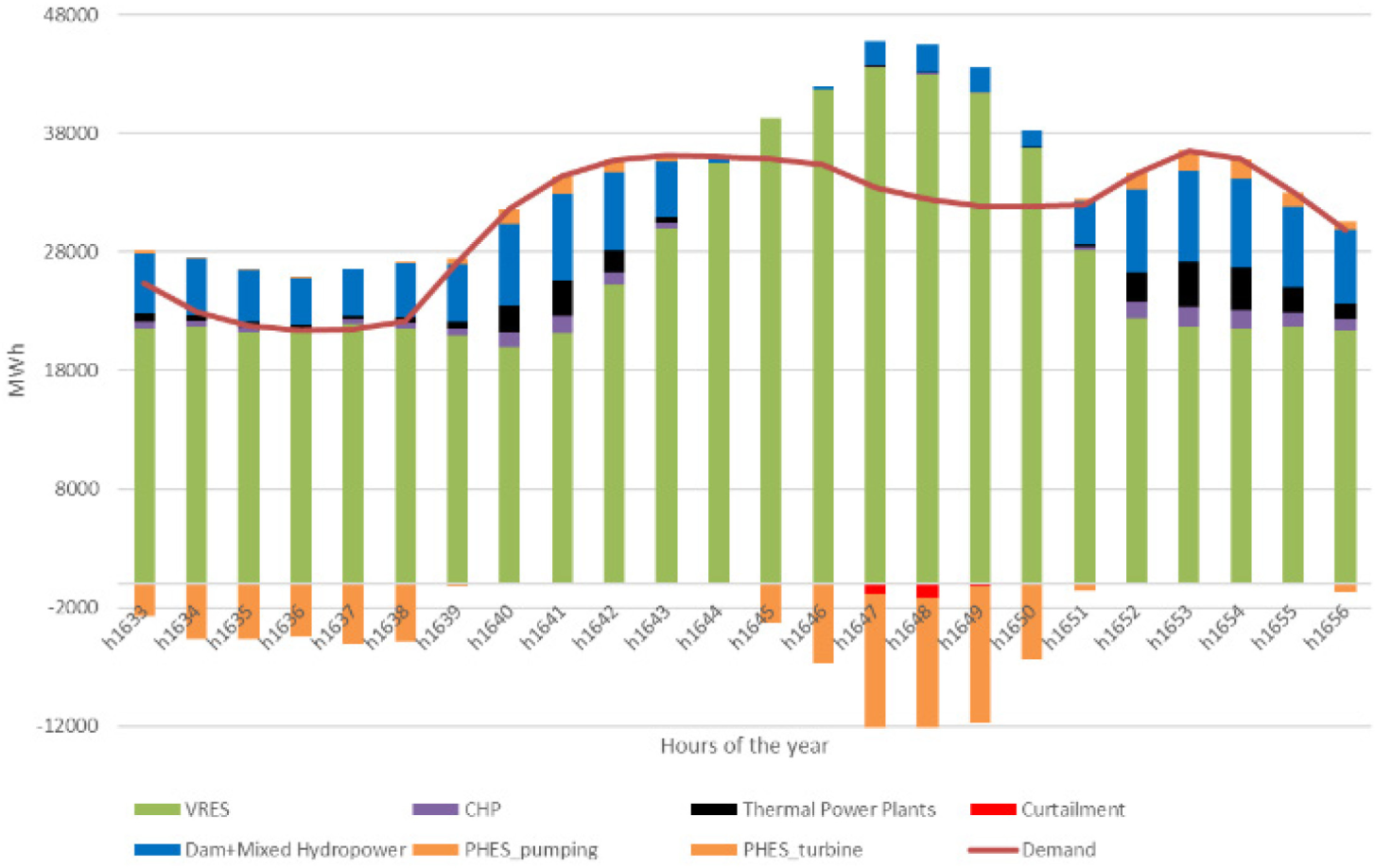
Hourly results reflect additional information. For instance, Figure 8 depicts the simulation with the historical conditions of 2020 at day 69 in 2030. Wind and solar contribute every hour, increasing during the daytime. In hours with low levels of renewables, thermal power plants increased the generation, whose hourly-average maximum ramp-up would increase by 1699 MW, while the ramp-down would decrease by -1319 MW.
As mentioned in the methods section, PHES runs in over-productive and deficit hours, as h1639. This situation of witnessing pumping and turbine modes of the PHES units at the same time can be found in the real operation of the power system, given the large geographical area analyzed. However, it is important to note that this result is not derived from findings with a geographical tool, but from the statistical method applied to distribute the consumption of the pumping mode (PHES_pos_cons).
Hourly results from the dispatch allocation in hours 1633 to 1656 (day 69) of 2030 (proposal scenario). PHES in pumping mode is depicted in the negative axis, while PHES in turbine mode is in the positive axis
Climate change and energy security rely greatly on a deep decarbonization of the economy, supported by a transition in which the power system must strengthen the competition between the supply and demand sides of the energy system. This work contributes to this field, describing a method to overcome the gap between hourly and yearly dynamics in the same model framework. The HPSS model reproduces the expected problem of renewable variability in terms of curtailment and allows a wide range of technical modifications in both the demand and supply sides.
The initial conditions provided to a model are crucial, since the results of the outputs may radically change in long-term scenarios. In order to evaluate how the initial conditions influence the HPSS model, four sets have been implemented based on the historical data (2017-2020). These years have shown a great variability between them, such as dry seasons (2017) or social isolations (2020).
As a case study, Spain has verified the approach with real data, providing insights into such calibration parameters as the low PHES and grid efficiencies, or the competition between traditional hydropower and gas turbines for the first position generating electricity, a system which has become more and more competitive since 2017. Specifically, the technical flexibility and maturity of PHES in deregulated and centralized markets makes this technology prominent in decarbonization pathways, which means we need to focus on new efforts for a complete regulation framework of the increasing “negative residual load demand” market.
The simulation of the NECP’s objective scenario in this work finds a renewable penetration far from the goal of 74%. However, some measures are proposed as alternatives to the official report in order to reach the goal. Among others, a stationary electricity demand, the decommissioning of non-dispatchable nuclear power plants, and the expansion of VRES capacities according to an optimal wind-solar ratio, as well as making the mix more adequate for the regional climate conditions.
In comparison to other methods, the proposal effectively integrates hourly constraints into the annual generation, without linking to external software, which makes them relatively fast for calculations, while also providing reasonable accuracy in the results. By introducing the approach between the final and primary energy in the transformation chain of an IAM, the users could analyze the effects of alternatives related to capacity expansion, different prioritizations, as well as constraints from other areas such as land and water uses, or dynamic economic developments.
Finally, there is a potential to overcome the limitations in the model that constitutes further work. First, to improve the accuracy of the historical period at the hourly level; with special attention being paid to the PHES and the application of the flexibility parameter (fp) for dispatchable power plants, including international interconnections and nuclear power plants. Second, more technologies could be included to compete in over-productive hours. Third, a bottom-up approach can be studied for the hourly profile of electricity demand from different economic agents (industries, services, the energy sector). Finally, to expand the flexibilities and agents available for an assessment with a holistic approach based on the concept of smart energy systems.
This work has been supported by the project LOCOMOTION, funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program, under grant agreement No 821105. All the authors gratefully thank Mohamed Lifi and Alan Hynds for their language corrections and writing suggestions.
Gonzalo Parrado-Hernando: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Formal analysis, Writing-Original Draft, Visualization.
Fernando Frechoso-Escudero: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Luis Javier Miguel González: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
| AEM | Agencia Estatal de Meteorología (National Agency of Meteorology) |
| CCGT | Combined cycle gas turbine |
| CHP | Combined heat and power |
| D | Demand |
| E | Export |
| ESIO | REE data platform |
| fp | Flexibility parameter |
| G | generation |
| HPSS | Hourly power system subscript mode |
| I | Import |
| IAM | Integrated assessment model |
| IC | Installed capacity |
| IPCC | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change |
| LCOE | Levelized cost of electricity |
| NECP | National integrated energy and climate plan |
| N | Nuclear |
| PHES | Pump hydropower energy storage |
| PP | Thermal power plant |
| PHES_pos_turb | Electricity delivery from PHES storage to the grid |
| PHES_pos_cons | Electricity used to save energy in PHES storage |
| PHES_neg_turb | Electricity pumped from negative residual loads |
| LD_2nd_al | Load demand after PHES management |
| PRL2h | PRL after PHES management |
| ParCalDatabase | Parameter to calibrate historical final energy demands |
| PRL | Positive residual load |
| REE | Red Eléctrica de España (Spanish power system operator) |
| RL | Residual load |
| T&D | Transmission and distribution (power grid) |
| VRES | Variable renewable energy source |
- ,
European Court of Justice ,Eur. J. Health Law , Vol. 22 (5),pp 508–516 , 2015, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1163/15718093-12341375 - ,
Energy Research & Social Science From the geopolitics of oil and gas to the geopolitics of the energy transition : Is there a role for European supermajors? ,Energy Res. Soc. Sci. , Vol. 88 (April),pp 102634 , 2022, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2022.102634 - ,
Pathways to Overcoming Natural Gas Dependency on Russia—The German Case ,Energies , Vol. 15 (14),pp 1–24 , 2022, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/en15144939 - ,
Pandemic, War, and Global Energy Transitions ,Energies , Vol. 15 (17),pp 6114 , 2022, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/en15176114 - ,
Exploring the possibility space: taking stock of the diverse capabilities and gaps in integrated assessment models ,Environ. Res. Lett. , Vol. 16 (5), 2021, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/abe5d8 - ,
Limits to growth redux: A system dynamics model for assessing energy and climate change constraints to global growth ,Energy Policy , Vol. 120 (May),pp 514–525 , 2018, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.05.053 - ,
Integrated modeling of human-earth system interactions: An application of GCAM-fusion ,Energy Econ. , Vol. 103 (September),pp 105566 , 2021, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105566 - ,
MEDEAS: A new modeling framework integrating global biophysical and socioeconomic constraints ,Energy Environ. Sci. , Vol. 13 (3),pp 986–1017 , 2020, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ee02627d - ,
Dynamic Energy Return on Energy Investment (EROI) and material requirements in scenarios of global transition to renewable energies ,Energy Strateg. Rev. , Vol. 26 (September),pp 100399 , 2019, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2019.100399 - ,
1.5 °C degrowth scenarios suggest the need for new mitigation pathways ,Nat. Commun. , Vol. 12 (1),pp 1–16, 2021 , , https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22884-9 - , Integrated MARKAL-EFOM System (TIMES) Model for Energy Sector Modeling, 2020 IEEE 61st Annu. Int. Sci. Conf. Power Electr. Eng. Riga Tech. Univ. RTUCON 2020 - Proc., 2020
- ,
The importance of temporal resolution in modeling deep decarbonization of the electric power sector ,Environ. Res. Lett. , Vol. 16 (8), 2021, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ac10df - ,
Do multi-sector energy system optimization models need hourly temporal resolution? A case study with an investment and dispatch model applied to France ,Appl. Energy , Vol. 305 (April 2021),pp 117951 , 2022, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.117951 - ,
The importance of temporal resolution in modeling deep decarbonization of the electric power sector ,Environ. Res. Lett. , Vol. 16 (084005), 2021, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ac10df - ,
Smart energy and smart energy systems ,Energy , Vol. 137 ,pp 556–565 , 2017, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.05.123 - ,
A review of criticisms of integrated assessment models and proposed approaches to address these, through the lens of BECCs ,Energies , Vol. 12 (9),pp 1–21 , 2019, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/en12091747 - ,
The role of sustainable bioenergy in a fully decarbonised society ,Renew. Energy , Vol. 196 ,pp 195–203 , 2022, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.06.026 - ,
Evaluation of a proposal for reliable low-cost grid power with 100 % wind, water, and solar ,pp 3–8 , 2017, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1610381114/-/DCSupplemental.www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1610381114 - ,
Flexible electricity generation, grid exchange and storage for the transition to a 100% renewable energy system in Europe ,Renew. Energy , Vol. 139 ,pp 80–101 , 2019, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.02.077 - ,
Comparing electricity production costs of renewables to fossil and nuclear power plants in G20 countries ,Technical report. Greenpeace Deutschland , 2017 - ,
EROI analysis for direct coal liquefaction without and with CCS: The case of the Shenhua DCL Project in China ,Energies , Vol. 8 (2),pp 786–807 , 2015, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/en8020786 - ,
D4.1 (D13) Global Model: MEDEAS-World Model and IOA implementation at global geographical level ,Medeas-Ue , Vol. 1 (691287),pp 1–254 , 2017 - ,
Capturing features of hourly-resolution energy models through statistical annual indicators ,Renew. Energy , Vol. 197 ,pp 1192–1223 , 2022, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.07.040 - ,
Analysis of the variable renewable energy in the Spanish power system based on kernel probabilistic distributions ,Dyna , Vol. 96 (2),pp 179–185 , 2021, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.6036/9892 - ,
Optimizing cropping pattern to improve the performance of irrigation network using system dynamics—Powell algorithm ,Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. ,pp 64547–64559 , 2022, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20335-6 - , Subscript-Based Geospatial Migration Dynamics, 36th Int. Conf. Syst. Dyn. Soc., 2018
- Vensim documentation, 2022, https://www.vensim.com/documentation/index.html
- , Power System Stability and Control, 2022
- ,
Decarbonizing global power supply under region-specific consideration of challenges and options of integrating variable renewables in the REMIND model ,Energy Econ. , Vol. 64 ,pp 665–684 , 2017, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2016.05.012 - ,
Review of the operational flexibility and emissions of gas- and coal-fired power plants in a future with growing renewables ,Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. , Vol. 82 (July 2017),pp 1497–1513 , 2018, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.278 - ,
Trends and challenges in the operation of pumped-storage hydropower plants ,Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. , Vol. 44 ,pp 767–784 , 2015, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.01.029 - ,
Joint energy and reserve markets: Current implementations and modeling trends ,Electr. Power Syst. Res. , Vol. 109 ,pp 101–111 , 2014, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2013.12.013 - ,
Operating Hydroelectric Plants and Pumped Storage Units in a Competitive Environment ,Electr. J. , Vol. 6190 (00),pp 24–32 , 2000, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S1040-6190(00)00093-2 - ,
On the History and Future of 100% Renewable Energy Systems Research ,IEEE Access , Vol. 10 (July),pp 78176–78218 , 2022, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3193402 - ,
Critical Review of Data, Models and Performance Metrics for Wind and Solar Power Forecast ,IEEE Access , Vol. 10 ,pp 667–688 , 2022, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3137419 - ,
Forecasting the inevitable: A review on the impacts of climate change on renewable energy resources ,Sustain. Energy Technol. Assessments , Vol. 52 (PC),pp 102283 , 2022, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2022.102283 - ,
Climate change impacts on renewable energy supply ,Nat. Clim. Chang. , Vol. 11 (2),pp 119–125 , 2021, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-020-00949-9 - Energy balances, 2022, https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/energy/data/energy-balances
- Base de datos ESIOS, https://www.esios.ree.es/es
- Climatological summaries. Spain, 2022, https://www.aemet.es/es/serviciosclimaticos/vigilancia_clima/resumenes?w=0&datos=0&n=4
- Report of Energy Statistics of Cogeneration, 2018, https://www.aemet.es/es/serviciosclimaticos/vigilancia_clima/resumenes?w=0&datos=0&n=4
- Report of the Power System, 2022, https://www.ree.es/es/datos/publicaciones/informe-anual-sistema
- ,
An efficient method for finding the minimum of a function of several variables without calculating derivatives ,Comput. J. , Vol. 7 (2),pp 155–162 , 1964, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1093/comjnl/7.2.155 - ,
Metaheuristic optimization methods for calibration of system dynamics models ,J. Simul. , Vol. 12 (2),pp 190–209 , 2018, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1080/17477778.2018.1467850 - ,
Linked Sensitivity Analysis , Calibration , and Uncertainty Analysis Using a System Dynamics Model for Stroke Comparative Effectiveness Research , (November), 2016, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1177/0272989X16643940 - Calibration with Vensim, 2022, https://vensim.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/CalibrationWithVensim2022-pt1.pdf
- Integrated National Energy and Climate Plan 2021-2030 of Spain (English draft version), 2021, https://energy.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2019-06/ec_courtesy_translation_es_necp_0.pdf
- ,
Smart energy Denmark. A consistent and detailed strategy for a fully decarbonized society International Panel of Climate Change , Vol. 168 (June), 2022, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2022.112777 - ,
Forecasting and assessment of the 2030 australian electricity mix paths towards energy transition ,Energy , Vol. 205 ,pp 118020 , 2020, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118020 - ,
Cross-border energy exchange and renewable premiums: The case of the Iberian system ,Energies , Vol. 11 (12), 2018, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123277 - ,
A novel approach to represent the energy system in integrated assessment models ,Energy , Vol. 258 ,pp 124743 , 2022, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.124743 - ,
Impact of high penetration of wind and solar PV generation on the country power system load : The case study of Croatia , Vol. 184 ,pp 1470–1482 , 2016, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.06.099 - ,
Increasing the integration of solar photovoltaics in energy mix on the road to low emissions energy system e Economic and environmental implications , Vol. 143 ,pp 1310–1317 , 2019, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.05.080 - ,
Reliability-based design sensitivity by efficient simulation ,Comput. Struct. , Vol. 83 (14),pp 1048–1061 , 2005, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2004.11.015




